Price Slippage in Cryptocurrency: Understanding and Mitigating its Impact
In the realm of cryptocurrency trading, price slippage is an unavoidable reality, often catching even the most seasoned traders off guard. But what exactly is price slippage, and why does it occur?
Understanding slippage is crucial for any crypto trader, as it can significantly affect the profitability and success of your trades. In this comprehensive guide, we will explain price slippage and its causes, differentiate between its positive and negative impacts, and provide practical tips on how to calculate and manage it effectively. So, let’s get right into it!
What is Price Slippage, and Why does it occur?

Price slippage in cryptocurrency occurs when there is a difference between the expected price of a trade and the actual price at which the trade is executed. This phenomenon is not unique to digital currencies; it is common in various financial markets. However, due to the inherent characteristics of the crypto market, slippage can be more pronounced. Let us explore the primary reasons why price slippage occurs:
- Market Volatility: Crypto markets are well known for their high volatility. Prices can move significantly within seconds due to various factors, including news releases, market sentiment shifts, or large trades. This rapid price movement means that the price of a cryptocurrency can change drastically between the time an order is placed and when it’s executed.
- Liquidity Levels: Liquidity refers to how easily an asset can be bought or sold in the market at a price close to the market rate. In cases where liquidity is low – for instance, in the markets for less popular cryptocurrencies – there might not be enough volume to fill an order at the expected price. This discrepancy between supply and demand can lead to slippage, with larger orders being particularly susceptible.
- Network Congestion: In some cases, particularly with cryptocurrencies that rely on a blockchain network for transaction processing, network congestion can delay transaction confirmations. This delay might lead to a difference in the price at the time of order creation and the time of execution.
Positive vs. Negative Slippage
When it comes to cryptocurrency trading, slippage can manifest in two forms: positive and negative. Both types have a significant impact on the outcome of your trades but in different ways. Here is what you should know:
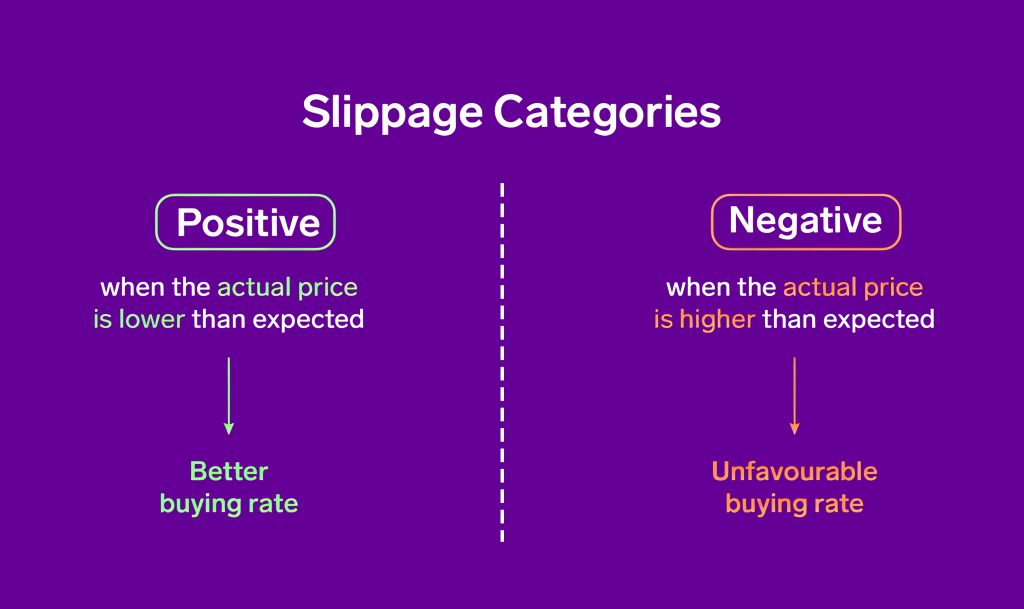
Positive Slippage
This occurs when a trade is executed at a better price than what was initially expected. For a buyer, this means purchasing a cryptocurrency at a lower price than anticipated, and for a seller, it involves selling at a higher price. Positive slippage often happens in fast-moving markets where the price improves in the favor of the trader’s position between the time the order is placed and when it is executed.
Negative Slippage
Conversely, negative slippage happens when a trade is executed at a worse price than expected. For buyers, this means paying more, and for sellers, receiving less. This type of slippage is typically observed during periods of high volatility when market orders are placed, and the market price moves unfavorably before the order is filled.
How Does Slippage Work?
To understand how slippage works, it is essential to look at the mechanics of executing a trade in the cryptocurrency market:
- Trade Initiation: When a trader places an order, be it a market order (executed immediately at the best available price) or a limit order (executed at a specified price or better), the market conditions at that exact moment dictate the initial expected price.
- Order Matching: In a highly liquid market, an order is more likely to be filled quickly and at the desired price. However, in a less liquid market or during volatile conditions, the order may not be filled immediately.
- Price Movement: If the market price changes significantly during the time gap between order placement and execution, slippage occurs. This is more common with market orders in volatile conditions, where prices can fluctuate rapidly.
- Order Execution: The final execution price of the order can be different from the expected price, leading to either positive or negative slippage.
For instance, if a trader places a market order to buy Bitcoin at a time when its price is rapidly rising, the order might be executed at a higher price than when the order was placed, resulting in negative slippage. Conversely, if the price begins to fall just as the order is placed, the trader might benefit from a lower purchase price, experiencing positive slippage.
How to Calculate Crypto Price Slippage
Calculating price slippage in cryptocurrency trading is a straightforward process. It involves comparing the price at which a trade was expected to be executed versus the actual execution price.
Formula for calculating slippage: To calculate the slippage percentage, subtract the expected price from the executed price, divide this difference by the expected price, and then multiply the result by 100.
Here is a step-by-step breakdown of how to find the price slippage:
- Start with the Executed Price: This is the actual price at which your trade was executed.
- Subtract the Expected Price: The Expected Price is the price at which you intended or expected the trade to occur at the time you placed the order.
- Divide the Result by the Expected Price: Take the difference you calculated by subtracting the Expected Price from the Executed Price, and then divide this number by the Expected Price.
- Multiply by 100 to Get the Percentage: Finally, multiply the result of the division by 100. This will give you the slippage percentage.
How to Avoid Slippage in Crypto
While it is impossible to completely eliminate slippage in cryptocurrency trading, there are strategies to minimize its impact. Here are some of the most effective strategies for avoiding slippage in crypto currency:
- Use Limit Orders: Unlike market orders, limit orders allow you to set a specific price at which you want to buy or sell. This control can help avoid slippage, especially in volatile markets.
- Trade During Peak Hours: Trading when the market is most active (usually when major markets overlap) can reduce slippage since higher trading volumes typically mean better liquidity.
- Avoid Large Orders in Thin Markets: Large orders in markets with low liquidity are more susceptible to slippage. Splitting large orders into smaller ones can help minimize this risk.
- Monitor Market Conditions: Being aware of current market conditions, including news and events that might cause volatility, allows you to adjust your trading strategy to minimize slippage.
- Use ‘Slippage Tolerances’: Some trading platforms allow you to set a slippage tolerance, specifying the maximum percentage of slippage you’re willing to accept. Orders will only be executed within these parameters.
- Choose Liquid Markets: Trading in more liquid markets or highly liquid cryptocurrency pairs can reduce the likelihood of significant slippage.
- Utilize Stop-Loss Orders: While not directly preventing slippage, stop-loss orders can help manage and limit potential losses due to unfavorable price movements.
Smart Trading in the Face of Slippage
At the end of the day, dealing with price slippage is a part of the crypto trading journey. However, armed with the right knowledge and strategies, you can navigate this aspect more confidently. It is about making smart choices in a market known for its quick changes. So, as you trade, remember to keep learning and stay informed to make the most of your trading experience.
