Understanding The Difference Between Centralized Exchange and Decentralized Exchange
When it comes to investing in cryptocurrency, having a firm grasp of the basics is essential for trading with confidence and security. At the heart of this knowledge is understanding the difference between centralized exchange and decentralized exchange. Why is this so vital? Because these platforms each have unique ways of operating and offer distinct trading experiences. So, join us as we dive into both exchanges, exploring how they work, their advantages and disadvantages, and what sets them apart.
What is a CEX or Centralized Exchange?
A centralized exchange, often referred to as a CEX, is a digital marketplace or platform where users can trade cryptocurrencies and digital assets with one another. Unlike decentralized exchanges (DEXs), which operate in a decentralized manner without a central authority, CEXs rely on a centralized organization to facilitate and oversee trading activities.

In a CEX, users typically create accounts, undergo verification processes (such as KYC or Know Your Customer checks), and deposit their assets into exchange-controlled wallets. The exchange acts as an intermediary, matching buy and sell orders, maintaining order books, and executing trades on behalf of users.
CEXs are known for their user-friendly interfaces, high liquidity due to significant trading volumes, and access to a wide range of trading tools and features. However, they are also susceptible to hacking and security breaches, as user funds are centralized and stored on the exchange’s servers.
Examples of Popular Centralized Exchanges
Some renowned CEXs include Coinbase, Binance, and Kraken. These platforms have earned their popularity owing to their user-friendly interfaces, robust security measures, and a wide range of supported cryptocurrencies and trading pairs. They also offer additional services like staking, lending, and more, enhancing the overall trading experience.
How Does A Centralized Crypto Exchange Work?
When using centralized exchanges (CEXs), users start by signing up and completing a verification process, often called KYC (Know Your Customer). Once verified, they can add money to their exchange accounts.
However, it is important to note that the exchange controls the private keys to the funds, essentially taking care of users’ assets. Users can then make trades using the exchange’s platform, and the exchange handles and confirms these transactions.
Pros and Cons of a Centralized Crypto Exchange
Centralized crypto exchanges (CEXs) have their own set of advantages and disadvantages. In this section, we will explore these pros and cons, providing a clear understanding of what CEXs offer and the challenges they pose for traders and investors.
Pros
- Enhanced liquidity due to higher trading volumes.
- User-friendly interfaces make them suitable for beginners.
- Faster transaction speeds.
- Access to a variety of trading tools and features.
Cons
- Susceptible to hacking and security breaches.
- Users do not maintain control over their private keys.
- Centralized management and operation.
- Often subject to strict regulatory requirements.
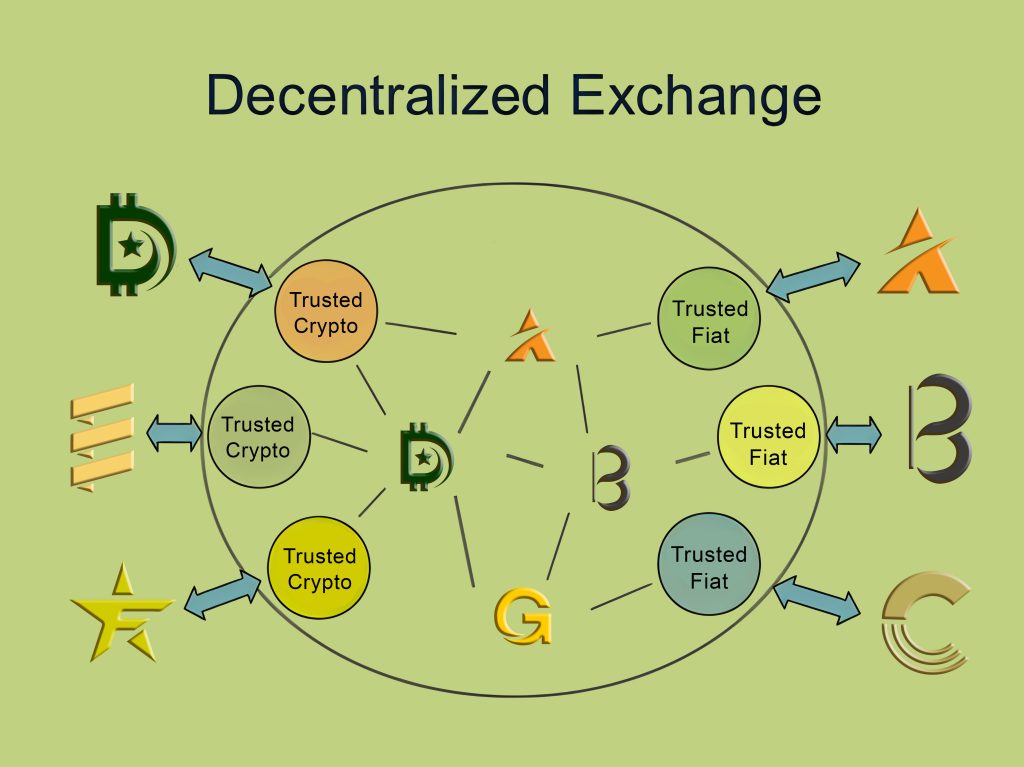
What Is a Dex or Decentralized Exchange?
A decentralized exchange, or DEX, is a blockchain-based platform where users can directly trade cryptocurrencies without a central intermediary. DEXs operate on smart contracts, thus allowing users to maintain control over their assets and private keys.
This decentralized approach emphasizes security and autonomy but may involve lower liquidity and user experience complexities compared to centralized exchanges. Investors are drawn here because DEXs offer benefits such as increased privacy and reduced hacking risk, aligning with blockchain principles. However, challenges also exist, including lower liquidity and usability complexities.
Popular Decentralized Exchanges for Crypto Trading
Uniswap, SushiSwap, and PancakeSwap are some of the popular DEXs. They stand out for their permissionless, anonymous trading features and are primarily built on Ethereum, allowing for a plethora of ERC-20 token trades.
How Does A Decentralized Crypto Exchange Work?
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) use smart contracts to automate and expedite the trading process. Users connect their cryptocurrency wallets directly to the exchange and execute trades from wallet to wallet. So, there is no need for account creation or identity verification, ensuring privacy and security.
Pros and Cons of a Decentralized Crypto Exchange
Just like a CEX, there are pros and cons of using a decentralized crypto exchange. These include:
Pros
- Users retain control over their funds and private keys.
- Enhanced privacy with no need for personal information.
- Reduced risk of large-scale hacks.
- Open-source and transparent operations.
Cons
- Lower liquidity compared to CEXs.
- Can be complex and intimidating for beginners.
- Slower transaction speeds due to network congestion.
Limited customer support
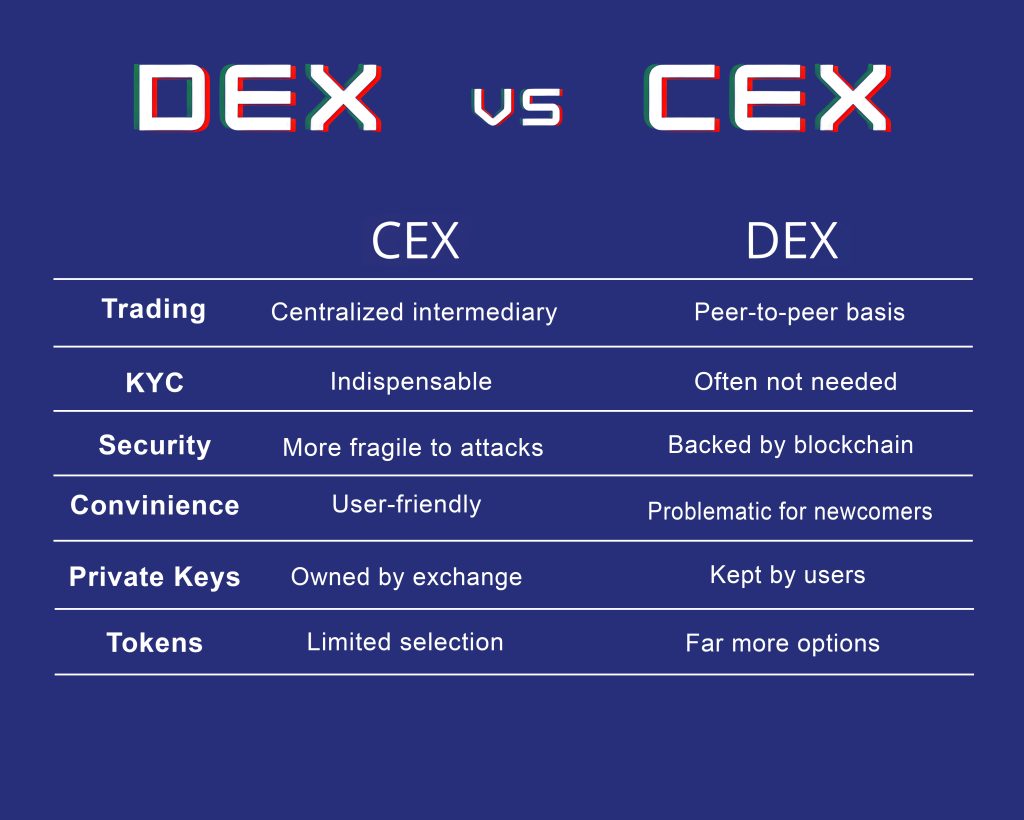
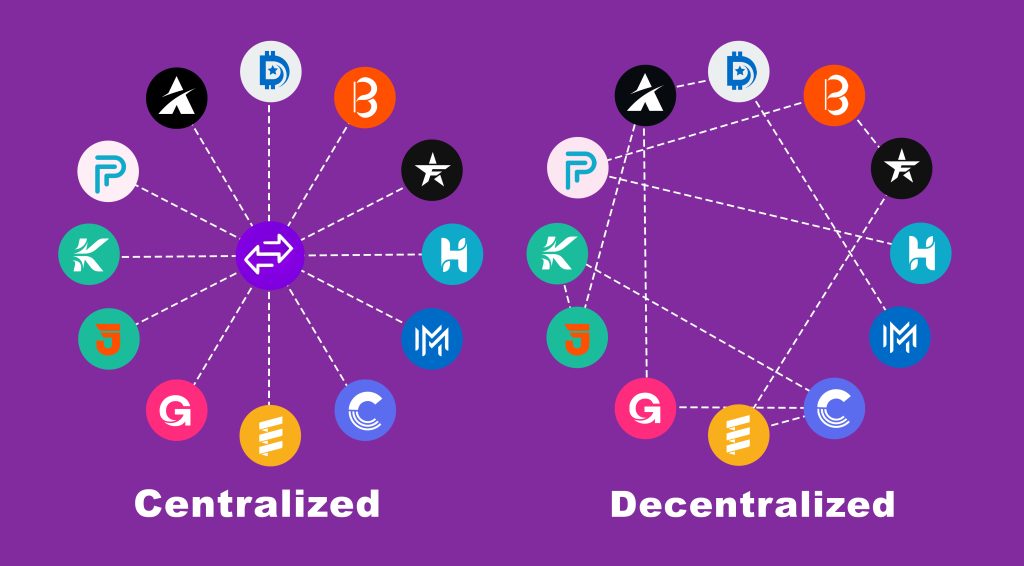
What Is the Difference Between CEX and DEX?
So, what is the difference between centralized exchange and decentralized exchange? Check out the simple breakdown below:
DEXs (Decentralized Exchanges):
- Operate without a central authority or intermediary.
- Enable direct peer-to-peer trading between users.
- Users retain control over their funds and private keys.
- Typically requires no account creation or identity verification.
- Emphasize security, privacy, and decentralization.
CEXs (Centralized Exchanges):
- Rely on a central organization to facilitate trades.
- Match buy and sell orders and execute transactions on behalf of users.
- Users often need to create accounts and undergo identity verification.
- Exchange manages custody of user assets, controlling private keys.
- Known for user-friendly interfaces, high liquidity, and regulatory compliance.
Understanding these distinctions can help users choose the exchange type that aligns with their preferences and priorities in cryptocurrency trading.
Closing Thoughts
Ultimately, recognizing the distinct characteristics of centralized and decentralized exchanges is pivotal for informed crypto trading. Each has unique pros and cons, so the best choice depends on individual preferences for security, privacy, and liquidity. As the landscape evolves, so will these platforms, continually enhancing the user experience.
